The PRISME team is composed of physicists, biochemists, biologists and radiotherapists. We specialize in multidisciplinary research aimed at developing, optimizing and controlling innovative radiotherapies, whether it be hadrontherapy or therapies using radioactive ion-emitting elements or nanoparticles. These radiotherapies aim to improve the treatment of certain cancers by increasing the effect of ionizing radiation in the tumor while minimizing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
Our multidisciplinary approach aims to quantify, understand and predict the effect of ionizing radiation on living organisms from processes induced at extremely short times (attosecond) at small scales (atomic nucleus) to long-term consequences (years) at the patient level.
We therefore design and carry out irradiation experiments on targets ranging from molecules or cells to small animals and patient samples (tumor, blood). These experiments feed an important part of our activity which consists in modeling the effects of radiation on living organisms.
One of the innovative techniques of radiotherapy is hadrontherapy, which is to send
an ion beam on the tumors to destroy them. We are working, in particular using simulations, data processing and predictions, to improve these systems by having on-line control over irradiation using dedicated detectors. These tools also have applications in imaging.
The activities can be divided into three research areas:
Axis 1 aims to develop simulations and detectors to control patient irradiation by detecting the particles emitted during hadrontherapy treatment. These developments also offer application prospects in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Axis 2 focuses on the development of multi-scale models and simulations to describe and predict the physical, chemical and biological processes induced by irradiation. It also develops irradiation and dosimetric control means for the measurement of radiobiological effects.
Axis 3 quantifies by experiment the effects induced by irradiation with molecular, cellular, multicellular, in-vitro or in-vivo systems. It focuses on the specificities of innovative radiotherapies and the personalization of care.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- L. Finco. Low mass Higgs searches in gamma-gamma at CMS. Lake Louise Winter Institute, Feb 2018, Lake Louise, Canada. ⟨hal-02071477⟩
- G. Boudoul. Stub simulation and cabling map in CMSSW. CMS Phase II Tracker Backend SysDev Workshop, Feb 2018, Abingdon, United Kingdom. ⟨in2p3-02014271⟩
- F. Berthias, Paul Bertier, T. Salbaing, L. Feketeová, H. Abdoul-Carime, et al.. Out of equilibrium dynamics of water nanodroplets. XXI Symposium on Atomic, Cluster and Surface Physics (SASP XXI), Feb 2018, Obergurgl, Austria. ⟨in2p3-02098107⟩
- R. Meissner, S. Denifl, L. Feketeová. Low energy electron interactions with nimorazole. XXI Symposium on Atomic, Cluster and Surface Physics (SASP XXI), Feb 2018, Obergurgl, Austria. ⟨in2p3-02098112⟩
- R. Meissner, S. Denifl, L. Feketeová. Recent results in imaging SN2 and E2 reaction dynamics. XXI Symposium on Atomic, Cluster and Surface Physics (SASP XXI), Feb 2018, Obergurgl, Austria. ⟨in2p3-02098122⟩
- Michel Farizon. Out of equilibrium dynamics of water nanodroplets. XXIst Symposium on Atomic, Cluster and Surface Physics 2018 (SASP 2018), Feb 2018, Obergurgl, Austria. ⟨in2p3-02072395⟩
- J. Baillet, S. Gavarini, N. Millard-Pinard, V. Garnier, C. Peaucelle, et al.. Surface damage on polycrystalline
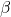 -SiC by xenon ion irradiation at high fluence. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 503, pp.140-150. ⟨10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.01.026⟩. ⟨cea-01701709⟩
-SiC by xenon ion irradiation at high fluence. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2018, 503, pp.140-150. ⟨10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.01.026⟩. ⟨cea-01701709⟩ - Tommi Alanne, Nicolas Bizot, Giacomo Cacciapaglia, Francesco Sannino. Classification of NLO operators for composite Higgs models. Physical Review D, 2018, 97 (7), pp.075028. ⟨10.1103/PhysRevD.97.075028⟩. ⟨hal-01704972⟩
- D. Autiero. DUNE et LBNF. Atelier Longbaseline, Jan 2018, Orsay, France. ⟨in2p3-02107270⟩
- Floriane Poignant, Benoit Gervais, Andrei Ipatov, Caterina Monini, Hela Charfi, et al.. Biophysical modelling of the radiosensitizing effect of high-Z nanoparticles. ARGENT - MSCA ITN - Advanced Radiotherapy, Generated by Exploiting Nanoprocesses and Technologies, Jan 2018, Paris, France. ⟨hal-01713385⟩


