The PRISME team is composed of physicists, biochemists, biologists and radiotherapists. We specialize in multidisciplinary research aimed at developing, optimizing and controlling innovative radiotherapies, whether it be hadrontherapy or therapies using radioactive ion-emitting elements or nanoparticles. These radiotherapies aim to improve the treatment of certain cancers by increasing the effect of ionizing radiation in the tumor while minimizing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
Our multidisciplinary approach aims to quantify, understand and predict the effect of ionizing radiation on living organisms from processes induced at extremely short times (attosecond) at small scales (atomic nucleus) to long-term consequences (years) at the patient level.
We therefore design and carry out irradiation experiments on targets ranging from molecules or cells to small animals and patient samples (tumor, blood). These experiments feed an important part of our activity which consists in modeling the effects of radiation on living organisms.
One of the innovative techniques of radiotherapy is hadrontherapy, which is to send
an ion beam on the tumors to destroy them. We are working, in particular using simulations, data processing and predictions, to improve these systems by having on-line control over irradiation using dedicated detectors. These tools also have applications in imaging.
The activities can be divided into three research areas:
Axis 1 aims to develop simulations and detectors to control patient irradiation by detecting the particles emitted during hadrontherapy treatment. These developments also offer application prospects in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Axis 2 focuses on the development of multi-scale models and simulations to describe and predict the physical, chemical and biological processes induced by irradiation. It also develops irradiation and dosimetric control means for the measurement of radiobiological effects.
Axis 3 quantifies by experiment the effects induced by irradiation with molecular, cellular, multicellular, in-vitro or in-vivo systems. It focuses on the specificities of innovative radiotherapies and the personalization of care.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- M. Gouzevitch. HH->bbbb boosted. 3rd CMS HH Workshop, Apr 2018, Paris, France. ⟨hal-02076991⟩
- O. Stézowski. AGATA-GRETINA Processing and Neural Networks. Second AGATA-GRETINA tracking arrays collaboration meeting, Apr 2018, Orsay, France. ⟨in2p3-02101706⟩
- S. Curtoni, L. Abbassi, A. Bès, G. Bosson, J. Collot, et al.. Development of a Beam Tagging Diamond Hodoscope for Online Ion Range Verification in Hadrontherapy. Forum de la recherche en Cancérologie 2018, Apr 2018, Villeurbanne, France. 2018. ⟨hal-01990640⟩
- Giovanna Muggiolu, Sarah Libert, Alexandra Lauret, Philippe Céruse, Christian Adrien Righini, et al.. Stratification of Head and Neck Cancers: DNA Repair Enzyme Signature to Identify Resistance and Toxicity Biomarkers. Forum de la recherche en Cancérologie 2018, Apr 2018, Villeurbanne, France. ⟨hal-01990547⟩
- Gersende Alphonse, Marie-Anne Chanrion, Micaela Cunha, Caterina Monini, Floriane Poignant, et al.. Interaction des radiations ionisantes avec les systèmes biologiques : modélisation multi-échelle pour comprendre et optimiser les radiothérapies innovantes. Forum de la recherche en Cancérologie 2018, Apr 2018, Villeurbanne, France. ⟨hal-01989434⟩
- L. Sarrasin, C. Panetier, C. Gaillard, Y. Pipon, N. Moncoffre. Effect of high temperature on the behavior of Mo and Cs in UO
 and UO
and UO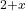 . MRS spring meeting, Apr 2018, Phenix, United States. ⟨in2p3-02097921⟩
. MRS spring meeting, Apr 2018, Phenix, United States. ⟨in2p3-02097921⟩ - D. Autiero. Status of WP8 Large Cryogenic Liquid Detectors. AIDA−2020 4th Annual Meeting, Apr 2018, Oxford, United Kingdom. ⟨in2p3-02107200⟩
- D. Caiulo. Charge readout and dual-phase technology. AIDA−2020 4th Annual Meeting, Apr 2018, Oxford, United Kingdom. ⟨in2p3-02107203⟩
- Caterina Monini, Micaela Cunha, Etienne Testa, Michaël Beuve. Study of the Influence of NanOx Parameters. Cancers, 2018, 10 (4), ⟨10.3390/cancers10040087⟩. ⟨hal-01919767⟩
- D. Tsimpis. Quartic fermions in IIA superspace. Recent developments in high energy theory and cosmology, Mar 2018, Athènes, Greece. ⟨hal-02063767⟩


