The PRISME team is composed of physicists, biochemists, biologists and radiotherapists. We specialize in multidisciplinary research aimed at developing, optimizing and controlling innovative radiotherapies, whether it be hadrontherapy or therapies using radioactive ion-emitting elements or nanoparticles. These radiotherapies aim to improve the treatment of certain cancers by increasing the effect of ionizing radiation in the tumor while minimizing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
Our multidisciplinary approach aims to quantify, understand and predict the effect of ionizing radiation on living organisms from processes induced at extremely short times (attosecond) at small scales (atomic nucleus) to long-term consequences (years) at the patient level.
We therefore design and carry out irradiation experiments on targets ranging from molecules or cells to small animals and patient samples (tumor, blood). These experiments feed an important part of our activity which consists in modeling the effects of radiation on living organisms.
One of the innovative techniques of radiotherapy is hadrontherapy, which is to send
an ion beam on the tumors to destroy them. We are working, in particular using simulations, data processing and predictions, to improve these systems by having on-line control over irradiation using dedicated detectors. These tools also have applications in imaging.
The activities can be divided into three research areas:
Axis 1 aims to develop simulations and detectors to control patient irradiation by detecting the particles emitted during hadrontherapy treatment. These developments also offer application prospects in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Axis 2 focuses on the development of multi-scale models and simulations to describe and predict the physical, chemical and biological processes induced by irradiation. It also develops irradiation and dosimetric control means for the measurement of radiobiological effects.
Axis 3 quantifies by experiment the effects induced by irradiation with molecular, cellular, multicellular, in-vitro or in-vivo systems. It focuses on the specificities of innovative radiotherapies and the personalization of care.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- E. Elbaz. Quark and lepton generation in the geometrical Rishon model. Physical Review D, 1986, 34, pp.1612-1618. ⟨in2p3-00004205⟩
- D.E. Medjadi, P. Quentin, M. Meyer, J. Libert. A microscopic approach to the coupling of collective and individual degrees of freedom to describe low energy excitations of odd-even nuclei. Physics Letters B, 1986, 181, pp.185-190. ⟨10.1016/0370-2693(86)90028-6⟩. ⟨in2p3-00001604⟩
- J. Alarja, A. Dauchy, A. Giorni, C. Morand, E. Pollaco, et al.. Charged particles identification with a csi(tl) scintillator. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1986, 242, pp.352-354. ⟨10.1016/0168-9002(86)90232-9⟩. ⟨in2p3-00013325⟩
- C. Baglin, S. Baird, G. Bassompierre, G. Borreani, J.C. Brient, et al.. Search for the
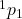 charmonium state in
charmonium state in 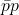 annihilations at the CERN intersecting storage rings. Physics Letters B, 1986, 171, pp.135-141. ⟨in2p3-00013411⟩
annihilations at the CERN intersecting storage rings. Physics Letters B, 1986, 171, pp.135-141. ⟨in2p3-00013411⟩ - N. Moncoffre. Caracterisation physico-chimique de la surface d'aciers implantes en ions azote. Chemical Physics [physics.chem-ph]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 1986. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨in2p3-00014188⟩
- S. Ouaskit. Recherche d'effets de sillage sur la charge de fragments issus de la dissociation dans une feuille mince d'ions moleculaires rapides. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 1986. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨in2p3-00014187⟩
- B. Mayer, J.M. Durand, R. Bertini, H. Catz, G.P. Gervino, et al.. Large variation in the backward angles analyzing power of the
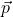 D
D 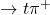 reaction around 1 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1986, 181, pp.25-27. ⟨10.1016/0370-2693(86)91247-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00004586⟩
reaction around 1 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1986, 181, pp.25-27. ⟨10.1016/0370-2693(86)91247-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00004586⟩ - J. Meyer, J. Bartel, M. Brack, P. Quentin. A gaussian parametrisation of the wigner transform of one-body density matrices. Iaea Topical Meeting On Phase Space Approach To Nuclear Dynamics, Sep 1985, Trieste, Italy. pp.491-495. ⟨in2p3-00000452⟩
- M. Ericson. Theoretical interpretation of the EMC effect. Topical European Meeting On Quark Structure Of Matter 1, Sep 1985, Strasbourg, France. pp.203-204. ⟨in2p3-00004348⟩
- J. Meyer. Résonances géantes à température finie. École thématique. Ecole Joliot Curie "La matière dans tout ses états", Bombannes, (France), du 16-20 septembre 1985 : 4ème session, 1985. ⟨cel-00639570⟩


