The PRISME team is composed of physicists, biochemists, biologists and radiotherapists. We specialize in multidisciplinary research aimed at developing, optimizing and controlling innovative radiotherapies, whether it be hadrontherapy or therapies using radioactive ion-emitting elements or nanoparticles. These radiotherapies aim to improve the treatment of certain cancers by increasing the effect of ionizing radiation in the tumor while minimizing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
Our multidisciplinary approach aims to quantify, understand and predict the effect of ionizing radiation on living organisms from processes induced at extremely short times (attosecond) at small scales (atomic nucleus) to long-term consequences (years) at the patient level.
We therefore design and carry out irradiation experiments on targets ranging from molecules or cells to small animals and patient samples (tumor, blood). These experiments feed an important part of our activity which consists in modeling the effects of radiation on living organisms.
One of the innovative techniques of radiotherapy is hadrontherapy, which is to send
an ion beam on the tumors to destroy them. We are working, in particular using simulations, data processing and predictions, to improve these systems by having on-line control over irradiation using dedicated detectors. These tools also have applications in imaging.
The activities can be divided into three research areas:
Axis 1 aims to develop simulations and detectors to control patient irradiation by detecting the particles emitted during hadrontherapy treatment. These developments also offer application prospects in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Axis 2 focuses on the development of multi-scale models and simulations to describe and predict the physical, chemical and biological processes induced by irradiation. It also develops irradiation and dosimetric control means for the measurement of radiobiological effects.
Axis 3 quantifies by experiment the effects induced by irradiation with molecular, cellular, multicellular, in-vitro or in-vivo systems. It focuses on the specificities of innovative radiotherapies and the personalization of care.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- D. Guinet, B. Chambon, B. Cheynis, A. Demeyer, D. Drain, et al.. Using the comibnation CsI(Tl) and photodiode for identification and energy measurement of light particles. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1989, 278, pp.614-616. ⟨10.1016/0168-9002(89)90889-9⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003761⟩
- N. El Khatib, H. Chermette, M. Maitrot. Electronic structure theoretical electronic properties of tetraphenyldithiapyranylidene dips phi-4 molecule and evaluation of the charge transfer occuring with doping agents like tncq. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 1989, 35, pp.339-358. ⟨in2p3-00013265⟩
- P. Bonche, S.J. Krieger, P. Quentin, M.S. Weiss, J. Meyer, et al.. Superdeformation and shape isomerism at zero spin. Nuclear Physics A, 1989, 500, pp.308-322. ⟨in2p3-00014653⟩
- R. Wada, D. Fabris, K. Hagel, G. Nebbia, Y. Lou, et al.. Temperatures and excitation energies of hot nuclei in the reactions of
 S + Ag and
S + Ag and 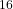 O + Ag at 30 MeV/nucleon. Physical Review C, 1989, 39, pp.497-515. ⟨10.1103/PhysRevC.39.497⟩. ⟨in2p3-00013323⟩
O + Ag at 30 MeV/nucleon. Physical Review C, 1989, 39, pp.497-515. ⟨10.1103/PhysRevC.39.497⟩. ⟨in2p3-00013323⟩ - M. El Kacimi. Preparation d'experiences a LEP avec le detecteur L3. Precalibration des cristaux de bgo du calorimetre electromagnetique a l'aide des rayons cosmiques. Etude des possibilites de mesure du nombre de familles de neutrinos par detection de photons isoles. High Energy Physics - Experiment [hep-ex]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 1989. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨in2p3-00013372⟩
- A. Brenac, M. Rebouillat, L. Porte. Mise au point d'un microscope à effet tunnel. Revue de Physique Appliquée, 1989, 24 (1), pp.117-131. ⟨10.1051/rphysap:01989002401011700⟩. ⟨jpa-00246020⟩
- F. Benrachi, B. Chambon, B. Cheynis, D. Drain, C. Pastor, et al.. Investigation of the performance of CsI(Tl) for charged particle identification by pulse-shape analysis. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1989, 281, pp.137-142. ⟨in2p3-00003759⟩
- N. Cue, J.-C. Poizat, J. Remillieux. Exciting the nucleus by target electron capture into atomic orbitals. EPL - Europhysics Letters, 1989, 8, pp.19-23. ⟨in2p3-00013258⟩
- M. Fahad. Moments nucleaires des isotopes de l'yttrium et relaxation de
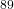 Y
Y . Nuclear Experiment [nucl-ex]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 1989. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨in2p3-00015155⟩
. Nuclear Experiment [nucl-ex]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 1989. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨in2p3-00015155⟩ - C. Baglin, S. Baird, G. Bassompierre, C. Biino, G. Borreani, et al.. Measurement of the
 cross section in pp annihilations at E
cross section in pp annihilations at E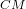 approximately = 3 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1989, 231, pp.557-562. ⟨in2p3-00018890⟩
approximately = 3 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1989, 231, pp.557-562. ⟨in2p3-00018890⟩


