The PRISME team is composed of physicists, biochemists, biologists and radiotherapists. We specialize in multidisciplinary research aimed at developing, optimizing and controlling innovative radiotherapies, whether it be hadrontherapy or therapies using radioactive ion-emitting elements or nanoparticles. These radiotherapies aim to improve the treatment of certain cancers by increasing the effect of ionizing radiation in the tumor while minimizing its harmful effects on healthy tissues.
Our multidisciplinary approach aims to quantify, understand and predict the effect of ionizing radiation on living organisms from processes induced at extremely short times (attosecond) at small scales (atomic nucleus) to long-term consequences (years) at the patient level.
We therefore design and carry out irradiation experiments on targets ranging from molecules or cells to small animals and patient samples (tumor, blood). These experiments feed an important part of our activity which consists in modeling the effects of radiation on living organisms.
One of the innovative techniques of radiotherapy is hadrontherapy, which is to send
an ion beam on the tumors to destroy them. We are working, in particular using simulations, data processing and predictions, to improve these systems by having on-line control over irradiation using dedicated detectors. These tools also have applications in imaging.
The activities can be divided into three research areas:
Axis 1 aims to develop simulations and detectors to control patient irradiation by detecting the particles emitted during hadrontherapy treatment. These developments also offer application prospects in the field of diagnostic imaging.
Axis 2 focuses on the development of multi-scale models and simulations to describe and predict the physical, chemical and biological processes induced by irradiation. It also develops irradiation and dosimetric control means for the measurement of radiobiological effects.
Axis 3 quantifies by experiment the effects induced by irradiation with molecular, cellular, multicellular, in-vitro or in-vivo systems. It focuses on the specificities of innovative radiotherapies and the personalization of care.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- CHERCHEURS NON-PERMANENTS / NON-PERMANENT RESEARCHERS:
- E. Galichet, F. Amorini, A. Anzalone, L. Auditore, V. Baran, et al.. Study of the quasi-projectile in
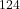 Sn +
Sn +  Ni and
Ni and 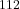 Sn +
Sn + 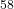 Ni reactions. International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics - IWM2005, Nov 2005, Catania, Italy. pp.147-155. ⟨in2p3-00087563⟩
Ni reactions. International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics - IWM2005, Nov 2005, Catania, Italy. pp.147-155. ⟨in2p3-00087563⟩ - P. Russotto, F. Amorini, A. Anzalone, L. Auditore, V. Baran, et al.. Recent progress in studying dynamical fragment production with CHIMERA. International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics - IWM2005, Nov 2005, Catania, Italy. pp.13-24. ⟨in2p3-00087497⟩
- R. Planeta, F. Amorini, A. Anzalone, L. Auditore, V. Baran, et al.. Isospin effects in neutron-rich and neutron-poor Sn+Ni systems. International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics - IWM2005, Nov 2005, Catania, Italy. pp.183-190. ⟨in2p3-00087564⟩
- M. Pârlog, S. Piantelli, G. Tabacaru. Estimation of freeze-out volumes in multifragmentation. International Workshop on Multifragmentation and related topics - IWM2005, Nov 2005, Catania, Italy. pp.263-270. ⟨in2p3-00087561⟩
- M. Farizon. Présentation d'ANAFIRE Plateau Technologique de l'IPN de Lyon “Analyse et Faisceaux d'Ions pour La Radiobiologie et l'Environnement". Première rencontre Franco-Marocaine de Radiochimie, Nov 2005, Casablanca, Morocco. ⟨in2p3-00401848⟩
- F. Gobet, S. Eden, B. Coupier, J. Tabet, B. Farizon, et al.. Biomolecular fragmentation induced by proton impact in the energy range of the Bragg peak.. Congrès international de Modélisation Moléculaire CIMM, Nov 2005, Casablanca, Morocco. ⟨in2p3-00024750⟩
- Philippe Lautesse. Méthodes de tri dans les collisions d'ions lourds aux énergies de Fermi et modes de désexcitation avec le multidétecteur INDRA. Physique Nucléaire Théorique [nucl-th]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 2005. ⟨tel-00127989⟩
- D. Davesne. Pion Superfluidity and Relativistic Hydrodynamics. Many-body Techniques at High Energies : Electroweak Scattering on Nuclei Versus the Physics of the QGP, Nov 2005, Trento, Italy. ⟨in2p3-00406383⟩
- B. Coupier. Studies towards the understanding of the effects of ionizing radiations at the molecular scales (20 to 150 keV H+/H + He Collisions; Dissociative Electron Attachment to Water). Nuclear Theory [nucl-th]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I; Université Leopold Franzens d'Innsbruck, 2005. English. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨tel-00012069⟩
- P. Jalade. Mesures et modelisation des effets radiobiologiques des ions legers sur des cellules tumorales humaines : application a l'hadrontherapie. Physique Nucléaire Théorique [nucl-th]. Université Claude Bernard - Lyon I, 2005. Français. ⟨NNT : ⟩. ⟨tel-00012047⟩


