Particle physics – study of the elementary constituents of matter – is one of IP2I’s main activities. Through the development of a calorimeter for the future linear accelerator, the direct measurement of antihydrogen acceleration due to Earth’s gravitation and the research conducted on the Higgs boson at the LHC, the FLC (CALICE), AEgIS and CMS teams are helping to assemble the puzzle for an understanding of our universe.
– – PAGE UNDER CONSTRUCTION – –
The team’s objective is to develop a high granularity hadronic calorimeter to equip future leptonic gas pedals. The calorimeter proposed for the FLC is entitled Semi-Digital Hadronic Calorimeter (SDHCAL). It uses RPC (resistive plate chamber) type gas detectors as active medium, read by integrated electronics with a granularity of 1cm2. The RPCs are inserted in a compact mechanical structure that acts as an absorber.
This type of calorimeter is used to measure the energy of the hadrons produced during collisions in particle gas pedals: on reaching the hadron calorimeter, they will deposit their energy in it by creating a sheaf of particles (called a jet) whose shape and size make it possible to identify it and measure its energy. The high granularity of the detector is therefore essential to increase its performance.
The team, with its partners, has built the first prototype of this new generation of calorimeters, as well as the associated electronics, and has designed Particle Flow Algorithms (PFA) to improve the reconstruction of the jets resulting from the interactions and to precisely measure their energy. Several tests at CERN have demonstrated the great power of SDHCAL.
The team contributed to the realization of the TOMUVOL detector for volcano tomography. It has developed a new reading scheme for large detectors with a reduced number of electronic channels while maintaining high granularity.
SDHCAL Prototype

Activities
- Organization of several beam tests of the SDHCAL prototype at CERN (2015, 16, 17 and 18) and exploitation of the data for the study of hadronic showers.
- Development of the full simulation of the SDHCAL prototype as well as the SDHCAL in ILD and CEPC.
- Design, construction and operation of the TOMUVOL detector with LPC.
- Design and realization of large RPC detectors (2 m2) and new reading electronics for module0 of SDHCAL for the ILD ILC project.
- Participation in the drafting of the ILD-ILC DBD and in the CDR of the CEPC project.
- Design and realization of the large reading cards for RPC chambers for the muon CMS upgrade project using timing.
- Design of a new ZDAQ acquisition system
- Design of a new reading card for gas detectors (PCT/EP2018/053561-EN3062926)
- Development of PFA algorithms (ArborPFA/APRIL)
- Development of a new material for RPC detectors to increase their detection rate by a factor of 1000.
- Design and realization of a detection system for homeland security for the company Smiths Detection based on the patent. Financing by PULSALYS.
- Co-organization of the CHEF conferences on calorimetry.
Interaction of a pion (left) and an electron (right) in SDHCAL
Measurement of hadron beam energy at CERN (left: linearity, right: resolution)

Knit Pads for Reading Gas Detectors (PCT/EP2018/053561-EN3062926)

The AEgIS (Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy) team at IP2I is working on the experiment of the same name carried out at CERN. The aim is to make the first direct measurement of the effects of gravitation on antimatter by observing the fall of antihydrogen atoms.
Researchers use antiprotons to produce a beam of antihydrogen atoms that is sent into a device called a Moire deflectometer. Combined with a position detector, this allows them to measure the magnitude of the gravitational interaction between matter (Earth) and antimatter (antihydrogen) to an accuracy of 1%.
The deflectometer is equipped with a grid system that divides the antihydrogen beam into parallel beams, creating a periodic structure whose analysis allows the deflection of the antihydrogen beam during its horizontal flight to be determined. By combining this measurement with the time of flight, we can then measure the gravitational force exerted on the antihydrogen atoms.
The AEgIS collaboration brings together physicists from all over Europe and faces many technical challenges such as the use of very low temperatures (0.1° K), ultra-vacuum (10-11 mbar), high magnetic fields (1 and 5 T), Lyman lasers α to characterize antihydrogen jets, the production of excited positronium, antiprotons, etc…
Our team built the hydrogen ion beam used to characterize the deflectometer’s moiré arrays.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- CHERCHEURS NON-PERMANENTS / NON-PERMANENT RESEARCHERS:
- M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Formation of the
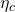 in Two-Photon Collisions at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 461, pp.155-166. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00784-4⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003666⟩
in Two-Photon Collisions at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 461, pp.155-166. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00784-4⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003666⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al..
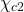 formation in two-photon collisions at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 453, pp.73-82. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00279-8⟩. ⟨in2p3-00014352⟩
formation in two-photon collisions at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 453, pp.73-82. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00279-8⟩. ⟨in2p3-00014352⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Searches for Scalar Quarks in
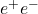 Interactions at
Interactions at  = 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 471, pp.308-320. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)01363-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003726⟩
= 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 471, pp.308-320. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)01363-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003726⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Search for the standard model Higgs boson in
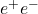 interactions at
interactions at  = 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 461, pp.376-386. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00853-9⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003674⟩
= 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 461, pp.376-386. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00853-9⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003674⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Measurement of the Spectroscopy of Orbitally Excited B Mesons at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 465, pp.323-334. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)01067-9⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003006⟩
- M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Heavy Quarkonium Production in Z Decays. Physics Letters B, 1999, 453, pp.94-106. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00280-4⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003490⟩
- M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Measurement of the
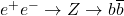 forward-backward asymmetry and the
forward-backward asymmetry and the 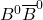 mixing parameter using prompt leptons. Physics Letters B, 1999, 448, pp.152-162. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(98)01601-3⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003513⟩
mixing parameter using prompt leptons. Physics Letters B, 1999, 448, pp.152-162. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(98)01601-3⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003513⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Search for heavy neutral and charged leptons in e
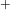 e
e annihilation at
annihilation at  = 183 and 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 462, pp.354-364. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(97)01074-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00023108⟩
= 183 and 189 GeV. Physics Letters B, 1999, 462, pp.354-364. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(97)01074-5⟩. ⟨in2p3-00023108⟩ - M. Acciarri, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, S. Ahlen, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Searches for Scalar Top and Scalar Bottom Quarks in
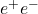 Interactions at 161 GeV
Interactions at 161 GeV 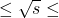 183 Gev. Physics Letters B, 1999, 445, pp.428-438. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(98)01505-6⟩. ⟨in2p3-00000251⟩
183 Gev. Physics Letters B, 1999, 445, pp.428-438. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(98)01505-6⟩. ⟨in2p3-00000251⟩ - M. Acciarri, P. Achard, O. Adriani, M. Aguilar-Benitez, J. Alcaraz, et al.. Measurement of Mass and Width of the W Boson at LEP. Physics Letters B, 1999, 454, pp.386-398. ⟨10.1016/S0370-2693(99)00348-2⟩. ⟨in2p3-00003526⟩

