The international collaboration ALICE (“A Large Ion Collider Experiment”), of which the eponymous research group of the IP2I in Lyon is a member, aims to study nuclear matter in a state of extremely high temperature, where the deconfinement of hadrons (including protons and neutrons) into plasma of quarks and gluons takes place.
Matter is made up of atoms, themselves made up of electrons surrounding a nucleus of protons and neutrons, the latter being formed of quarks, linked by gluons. No quark or gluon has ever been observed in isolation: they appear to be permanently bonded together and confined in composite particles. At temperatures 100,000 times higher than those at the centre of the Sun, they deconform to form a plasma, which would have existed a few microseconds after the Big Bang. This plasma is predicted by the fundamental theory of strong interaction, Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD), and its study allows us to understand the ultimate organization of matter subject to strong interaction and the very first moments of the universe.
The LHC collides lead ions to recreate conditions similar to those immediately after the Big Bang and form this quark and gluon plasma. For this infinitely small study, a huge detector has been built at the LHC. It is capable of measuring the particles emitted by the plasma as it expands and cools.
Our group has been involved in this construction and in obtaining major results in this field of physics.
The activities of the ALICE group of the IP2I of Lyon are twofold:
- the analysis of data collected in proton-proton, proton-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus collisions at the CERN LHC
- participation in the construction and operation of the forward vertex trajectograph, the Muon Forward Tracker
Analysis of data collected in proton-proton, proton-nucleus and nucleus-nucleus collisions at the CERN LHC
The physics analyses of the ALICE experiment carried out in the Lyon groups cover a wide range of subjects, from the light quark sector u, d, s with the study of the forward production of low mass vector mesons ![]() and
and ![]() in the dimuonic decay channel, to the heavy quarks sector c and b, with the study of the production of the quarkonium states of the
in the dimuonic decay channel, to the heavy quarks sector c and b, with the study of the production of the quarkonium states of the ![]() and
and ![]() families. This analytical work has already led to a number of remarkable results, notably through the study of collective phenomena characterizing the evolution of the
families. This analytical work has already led to a number of remarkable results, notably through the study of collective phenomena characterizing the evolution of the ![]() and
and ![]() mesons, namely the appearance of kinematic correlations between the
mesons, namely the appearance of kinematic correlations between the ![]() meson and light hadrons in high multiplicity proton-Pb collisions, and the observation of elliptical flow of the
meson and light hadrons in high multiplicity proton-Pb collisions, and the observation of elliptical flow of the ![]() meson compatible with zero in Pb-Pb collisions (behavior different from all the other particles studied).
meson compatible with zero in Pb-Pb collisions (behavior different from all the other particles studied).
Participation in the construction and operation of the forward vertex trajectograph, the Muon Forward Tracker
The group is also responsible for the construction and operation of the vertex forward trajectograph, the Muon Forward Tracker (MFT), one of the first applications in high energy physics of CMOS silicon pixel sensor technology. The MFT, which will be integrated into the ALICE detector starting with Run3 of the LHC (2021), is designed to enable precise measurement of the details of the vertex region for forward-produced particles, especially muons, whose different topologies and production processes can be studied.
NON-PERMANENTS:
- DOCTORANTS / DOCTORAL STUDENTS:
- CHERCHEURS NON-PERMANENTS / NON-PERMANENT RESEARCHERS:
- S. Acharya, Fernando Torales - Acosta, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Azimuthally-differential pion femtoscopy relative to the third harmonic event plane in Pb-Pb collisions at
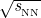 = 2.76 TeV. Physics Letters B, 2018, 785, pp.320-331. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.06.042⟩. ⟨hal-01768140⟩
= 2.76 TeV. Physics Letters B, 2018, 785, pp.320-331. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.06.042⟩. ⟨hal-01768140⟩ - S. Acharya, Fernando Torales - Acosta, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Anisotropic flow of identified particles in Pb-Pb collisions at
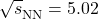 TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 09, pp.006. ⟨10.1007/JHEP09(2018)006⟩. ⟨hal-01801884⟩
TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 09, pp.006. ⟨10.1007/JHEP09(2018)006⟩. ⟨hal-01801884⟩ - Shreyasi Acharya, Fernando Torales - Acosta, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Measurements of low-p
 electrons from semileptonic heavy-flavour hadron decays at mid-rapidity in pp and Pb-Pb collisions at
electrons from semileptonic heavy-flavour hadron decays at mid-rapidity in pp and Pb-Pb collisions at 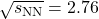 TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 10, pp.061. ⟨10.1007/JHEP10(2018)061⟩. ⟨hal-01801878⟩
TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 10, pp.061. ⟨10.1007/JHEP10(2018)061⟩. ⟨hal-01801878⟩ - Shreyasi Acharya, Fernando Torales - Acosta, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Inclusive J/
 production at forward and backward rapidity in p-Pb collisions at
production at forward and backward rapidity in p-Pb collisions at  = 8.16 TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 07, pp.160. ⟨10.1007/JHEP07(2018)160⟩. ⟨hal-01801876⟩
= 8.16 TeV. Journal of High Energy Physics, 2018, 07, pp.160. ⟨10.1007/JHEP07(2018)160⟩. ⟨hal-01801876⟩ - S. Acharya, Jaroslav Adam, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Longitudinal asymmetry and its effect on pseudorapidity distributions in Pb-Pb collisions at
 = 2.76 TeV. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 781, pp.20-32. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.03.051⟩. ⟨hal-01768021⟩
= 2.76 TeV. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 781, pp.20-32. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.03.051⟩. ⟨hal-01768021⟩ - Shreyasi Acharya, Jaroslav Adam, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, et al.. Production of deuterons, tritons,
 He nuclei and their antinuclei in pp collisions at
He nuclei and their antinuclei in pp collisions at 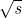 = 0.9, 2.76 and 7 TeV. Phys.Rev.C, 2018, 97 (2), pp.024615. ⟨10.1103/PhysRevC.97.024615⟩. ⟨hal-01724967⟩
= 0.9, 2.76 and 7 TeV. Phys.Rev.C, 2018, 97 (2), pp.024615. ⟨10.1103/PhysRevC.97.024615⟩. ⟨hal-01724967⟩ - Shreyasi Acharya, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, et al.. Production of
 He and
He and 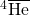 in Pb-Pb collisions at
in Pb-Pb collisions at  = 2.76 TeV at the LHC. Nucl.Phys.A, 2018, 971, pp.1-20. ⟨10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2017.12.004⟩. ⟨hal-01704400⟩
= 2.76 TeV at the LHC. Nucl.Phys.A, 2018, 971, pp.1-20. ⟨10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2017.12.004⟩. ⟨hal-01704400⟩ - D. Adamová, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, Michelangelo Agnello, Neelima Agrawal, et al.. J/
 production as a function of charged-particle pseudorapidity density in p-Pb collisions at
production as a function of charged-particle pseudorapidity density in p-Pb collisions at  TeV. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 776, pp.91-104. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2017.11.008⟩. ⟨hal-01669479⟩
TeV. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 776, pp.91-104. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2017.11.008⟩. ⟨hal-01669479⟩ - S. Acharya, A. Baldisseri, H. Borel, J. Castillo Castellanos, J.L. Charvet, et al.. First measurement of jet mass in Pb-Pb and p-Pb collisions at the LHC. Physics Letters B, 2018, 776, pp.249-264. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2017.11.044⟩. ⟨in2p3-01456785⟩
- Shreyasi Acharya, Dagmar Adamova, Jonatan Adolfsson, Madan Mohan Aggarwal, Gianluca Aglieri Rinella, et al.. Constraints on jet quenching in p-Pb collisions at
 = 5.02 TeV measured by the event-activity dependence of semi-inclusive hadron-jet distributions. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 783, pp.95-113. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.05.059⟩. ⟨hal-01833822⟩
= 5.02 TeV measured by the event-activity dependence of semi-inclusive hadron-jet distributions. Phys.Lett.B, 2018, 783, pp.95-113. ⟨10.1016/j.physletb.2018.05.059⟩. ⟨hal-01833822⟩

